搜索到
10
篇与
vpn
的结果
-
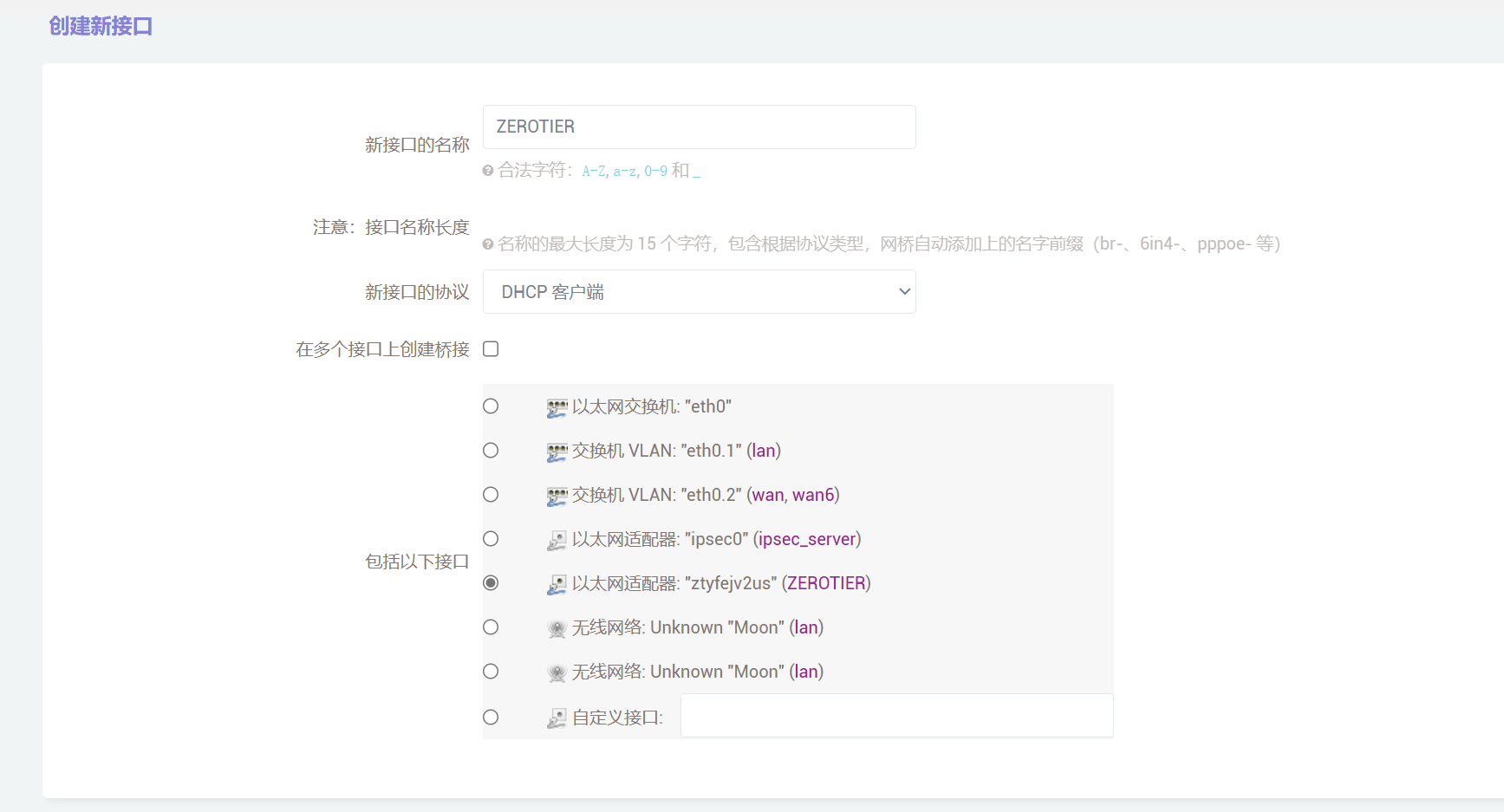
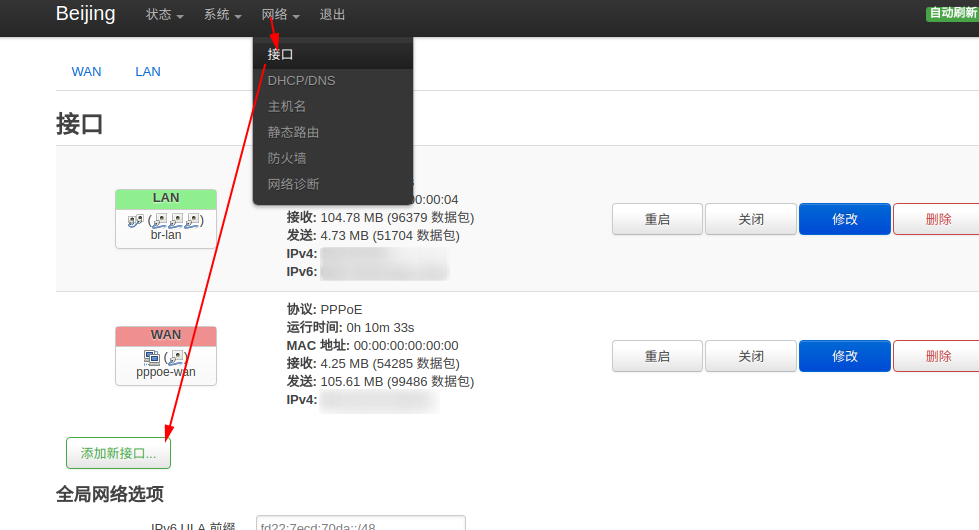
 【openwrt】通过zerotier网络连接路由器时,如何配置使用TYDD终端工具 一、创建新的接口命名为ZEROTIER,接口的协议选择DHCP客户端,接口选择已经连接的ZEROTIER适配器。修改刚刚创建的接口配置,防火墙设置,新建ZEROTIER防火墙,保存并应用二、配置防护墙端口转发配置7681端口转发,并选择ZEROTIER网络三、自定义规则iptables -I FORWARD -i ztyfejv2us -j ACCEPT iptables -I FORWARD -o ztyfejv2us -j ACCEPT iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -o ztyfejv2us -j MASQUERADE
【openwrt】通过zerotier网络连接路由器时,如何配置使用TYDD终端工具 一、创建新的接口命名为ZEROTIER,接口的协议选择DHCP客户端,接口选择已经连接的ZEROTIER适配器。修改刚刚创建的接口配置,防火墙设置,新建ZEROTIER防火墙,保存并应用二、配置防护墙端口转发配置7681端口转发,并选择ZEROTIER网络三、自定义规则iptables -I FORWARD -i ztyfejv2us -j ACCEPT iptables -I FORWARD -o ztyfejv2us -j ACCEPT iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -o ztyfejv2us -j MASQUERADE -
 如何在群晖 NAS 上使用 Docker 运行 ZeroTier 本文将指导您如何在群晖 NAS 上使用 Docker 运行 ZeroTier 容器,从而实现虚拟私有网络 (VPN) 的功能。ZeroTier 是一款开源的虚拟网络管理工具,可以将不同的设备连接到同一个虚拟网络中。前提条件确保您的群晖 NAS 允许 SSH 连接。确保 Docker 应用已在群晖 NAS 上安装并且运行正常。您需要一个有效的 ZeroTier 身份验证令牌。使用 ip tuntap 创建 TUN 设备由于群晖 NAS 并不直接支持 /dev/net/tun,您需要使用 ip tuntap 命令来创建 TUN 设备。请注意,群晖 NAS 的 ip tuntap 命令可能不可用,因此您需要采用其他方法来模拟 TUN 设备的功能。创建 TUN 设备加载 TUN 模块:sudo modprobe tun手动创建 TUN 设备:sudo ip tuntap add dev tun0 mode tun sudo ip link set tun0 up检查 TUN 设备状态检查 TUN 设备的状态:ip link show tun0创建 ZeroTier 容器为了在群晖 NAS 上运行 ZeroTier 容器,您需要使用以下命令。此命令已经过实践验证,并且在群晖 NAS 上可行。示例命令docker run -d \ --name ztclient \ --restart=always \ --device=/dev/net/tun \ --net=host \ --cap-add=NET_ADMIN \ --cap-add=SYS_ADMIN \ -v /volume1/docker/dockerfile/zerotier/ztclient/data:/var/lib/zerotier-one \ zerotier/zerotier-synology:1.8.10 \ -e ZT1_AUTH_TOKEN=<your_auth_token>命令解析-d: 以守护进程模式运行容器。--name ztclient: 为容器命名。--restart=always: 容器会在系统启动时自动重启。--device=/dev/net/tun: 挂载 /dev/net/tun 设备,以便容器能够使用 TUN 功能。--net=host: 使用宿主机网络栈,而不是 Docker 的默认网络栈。--cap-add=NET_ADMIN: 增加容器的权限,使其能够管理网络接口。--cap-add=SYS_ADMIN: 增加容器的权限,使其能够执行系统级操作。-v /volume1/docker/dockerfile/zerotier/ztclient/data:/var/lib/zerotier-one: 将宿主机上的目录挂载到容器内,用于持久化存储 ZeroTier 数据。zerotier/zerotier-synology:1.8.10: 指定要运行的 Docker 镜像及其版本。-e ZT1_AUTH_TOKEN=<your_auth_token>: 设置环境变量,其中 <your_auth_token> 是您的 ZeroTier 身份验证令牌。注意事项确保您已经创建了 /volume1/docker/dockerfile/zerotier/ztclient/data 目录。如果您遇到权限问题,可能需要使用 sudo 来运行 Docker 命令。如果您之前从未在群晖上使用过 Docker,您可能需要先使用 sudo 来执行 Docker 命令。如果您经常使用 Docker,可以考虑将您的用户添加到 docker 组,这样就不需要每次都使用 sudo。结论通过上述步骤,您应该能够在群晖 NAS 上成功运行 ZeroTier 容器。如果您需要进一步的帮助,请随时提问。
如何在群晖 NAS 上使用 Docker 运行 ZeroTier 本文将指导您如何在群晖 NAS 上使用 Docker 运行 ZeroTier 容器,从而实现虚拟私有网络 (VPN) 的功能。ZeroTier 是一款开源的虚拟网络管理工具,可以将不同的设备连接到同一个虚拟网络中。前提条件确保您的群晖 NAS 允许 SSH 连接。确保 Docker 应用已在群晖 NAS 上安装并且运行正常。您需要一个有效的 ZeroTier 身份验证令牌。使用 ip tuntap 创建 TUN 设备由于群晖 NAS 并不直接支持 /dev/net/tun,您需要使用 ip tuntap 命令来创建 TUN 设备。请注意,群晖 NAS 的 ip tuntap 命令可能不可用,因此您需要采用其他方法来模拟 TUN 设备的功能。创建 TUN 设备加载 TUN 模块:sudo modprobe tun手动创建 TUN 设备:sudo ip tuntap add dev tun0 mode tun sudo ip link set tun0 up检查 TUN 设备状态检查 TUN 设备的状态:ip link show tun0创建 ZeroTier 容器为了在群晖 NAS 上运行 ZeroTier 容器,您需要使用以下命令。此命令已经过实践验证,并且在群晖 NAS 上可行。示例命令docker run -d \ --name ztclient \ --restart=always \ --device=/dev/net/tun \ --net=host \ --cap-add=NET_ADMIN \ --cap-add=SYS_ADMIN \ -v /volume1/docker/dockerfile/zerotier/ztclient/data:/var/lib/zerotier-one \ zerotier/zerotier-synology:1.8.10 \ -e ZT1_AUTH_TOKEN=<your_auth_token>命令解析-d: 以守护进程模式运行容器。--name ztclient: 为容器命名。--restart=always: 容器会在系统启动时自动重启。--device=/dev/net/tun: 挂载 /dev/net/tun 设备,以便容器能够使用 TUN 功能。--net=host: 使用宿主机网络栈,而不是 Docker 的默认网络栈。--cap-add=NET_ADMIN: 增加容器的权限,使其能够管理网络接口。--cap-add=SYS_ADMIN: 增加容器的权限,使其能够执行系统级操作。-v /volume1/docker/dockerfile/zerotier/ztclient/data:/var/lib/zerotier-one: 将宿主机上的目录挂载到容器内,用于持久化存储 ZeroTier 数据。zerotier/zerotier-synology:1.8.10: 指定要运行的 Docker 镜像及其版本。-e ZT1_AUTH_TOKEN=<your_auth_token>: 设置环境变量,其中 <your_auth_token> 是您的 ZeroTier 身份验证令牌。注意事项确保您已经创建了 /volume1/docker/dockerfile/zerotier/ztclient/data 目录。如果您遇到权限问题,可能需要使用 sudo 来运行 Docker 命令。如果您之前从未在群晖上使用过 Docker,您可能需要先使用 sudo 来执行 Docker 命令。如果您经常使用 Docker,可以考虑将您的用户添加到 docker 组,这样就不需要每次都使用 sudo。结论通过上述步骤,您应该能够在群晖 NAS 上成功运行 ZeroTier 容器。如果您需要进一步的帮助,请随时提问。 -
 OpenVPN在linux中的命令 一、配置项OpenVPN 2.5.5 x86_64-pc-linux-gnu [SSL (OpenSSL)] [LZO] [LZ4] [EPOLL] [PKCS11] [MH/PKTINFO] [AEAD] built on Mar 22 2022 General Options: --config file : Read configuration options from file. --help : Show options. --version : Show copyright and version information. Tunnel Options: --local host : Local host name or ip address. Implies --bind. --remote host [port] : Remote host name or ip address. --remote-random : If multiple --remote options specified, choose one randomly. --remote-random-hostname : Add a random string to remote DNS name. --mode m : Major mode, m = 'p2p' (default, point-to-point) or 'server'. --proto p : Use protocol p for communicating with peer. p = udp (default), tcp-server, or tcp-client --proto-force p : only consider protocol p in list of connection profiles. p = udp6, tcp6-server, or tcp6-client (ipv6) --connect-retry n [m] : For client, number of seconds to wait between connection retries (default=5). On repeated retries the wait time is exponentially increased to a maximum of m (default=300). --connect-retry-max n : Maximum connection attempt retries, default infinite. --http-proxy s p [up] [auth] : Connect to remote host through an HTTP proxy at address s and port p. If proxy authentication is required, up is a file containing username/password on 2 lines, or 'stdin' to prompt from console. Add auth='ntlm' if the proxy requires NTLM authentication. --http-proxy s p 'auto[-nct]' : Like the above directive, but automatically determine auth method and query for username/password if needed. auto-nct disables weak proxy auth methods. --http-proxy-option type [parm] : Set extended HTTP proxy options. Repeat to set multiple options. VERSION version (default=1.0) AGENT user-agent --socks-proxy s [p] [up] : Connect to remote host through a Socks5 proxy at address s and port p (default port = 1080). If proxy authentication is required, up is a file containing username/password on 2 lines, or 'stdin' to prompt for console. --socks-proxy-retry : Retry indefinitely on Socks proxy errors. --resolv-retry n: If hostname resolve fails for --remote, retry resolve for n seconds before failing (disabled by default). Set n="infinite" to retry indefinitely. --float : Allow remote to change its IP address/port, such as through DHCP (this is the default if --remote is not used). --ipchange cmd : Run command cmd on remote ip address initial setting or change -- execute as: cmd ip-address port# --port port : TCP/UDP port # for both local and remote. --lport port : TCP/UDP port # for local (default=1194). Implies --bind. --rport port : TCP/UDP port # for remote (default=1194). --bind : Bind to local address and port. (This is the default unless --proto tcp-client or --http-proxy or --socks-proxy is used). --nobind : Do not bind to local address and port. --dev tunX|tapX : tun/tap device (X can be omitted for dynamic device. --dev-type dt : Which device type are we using? (dt = tun or tap) Use this option only if the tun/tap device used with --dev does not begin with "tun" or "tap". --dev-node node : Explicitly set the device node rather than using /dev/net/tun, /dev/tun, /dev/tap, etc. --lladdr hw : Set the link layer address of the tap device. --topology t : Set --dev tun topology: 'net30', 'p2p', or 'subnet'. --ifconfig l rn : TUN: configure device to use IP address l as a local endpoint and rn as a remote endpoint. l & rn should be swapped on the other peer. l & rn must be private addresses outside of the subnets used by either peer. TAP: configure device to use IP address l as a local endpoint and rn as a subnet mask. --ifconfig-ipv6 l r : configure device to use IPv6 address l as local endpoint (as a /64) and r as remote endpoint --ifconfig-noexec : Don't actually execute ifconfig/netsh command, instead pass --ifconfig parms by environment to scripts. --ifconfig-nowarn : Don't warn if the --ifconfig option on this side of the connection doesn't match the remote side. --route network [netmask] [gateway] [metric] : Add route to routing table after connection is established. Multiple routes can be specified. netmask default: 255.255.255.255 gateway default: taken from --route-gateway or --ifconfig Specify default by leaving blank or setting to "default". --route-ipv6 network/bits [gateway] [metric] : Add IPv6 route to routing table after connection is established. Multiple routes can be specified. gateway default: taken from --route-ipv6-gateway or 'remote' in --ifconfig-ipv6 --route-gateway gw|'dhcp' : Specify a default gateway for use with --route. --route-ipv6-gateway gw : Specify a default gateway for use with --route-ipv6. --route-metric m : Specify a default metric for use with --route. --route-delay n [w] : Delay n seconds after connection initiation before adding routes (may be 0). If not specified, routes will be added immediately after tun/tap open. On Windows, wait up to w seconds for TUN/TAP adapter to come up. --route-up cmd : Run command cmd after routes are added. --route-pre-down cmd : Run command cmd before routes are removed. --route-noexec : Don't add routes automatically. Instead pass routes to --route-up script using environmental variables. --route-nopull : When used with --client or --pull, accept options pushed by server EXCEPT for routes and dhcp options. --allow-pull-fqdn : Allow client to pull DNS names from server for --ifconfig, --route, and --route-gateway. --redirect-gateway [flags]: Automatically execute routing commands to redirect all outgoing IP traffic through the VPN. Add 'local' flag if both OpenVPN servers are directly connected via a common subnet, such as with WiFi. Add 'def1' flag to set default route using using 0.0.0.0/1 and 128.0.0.0/1 rather than 0.0.0.0/0. Add 'bypass-dhcp' flag to add a direct route to DHCP server, bypassing tunnel. Add 'bypass-dns' flag to similarly bypass tunnel for DNS. --redirect-private [flags]: Like --redirect-gateway, but omit actually changing the default gateway. Useful when pushing private subnets. --block-ipv6 : (Client) Instead sending IPv6 to the server generate ICMPv6 host unreachable messages on the client. (Server) Instead of forwarding IPv6 packets send ICMPv6 host unreachable packets to the client. --client-nat snat|dnat network netmask alias : on client add 1-to-1 NAT rule. --push-peer-info : (client only) push client info to server. --setenv name value : Set a custom environmental variable to pass to script. --setenv FORWARD_COMPATIBLE 1 : Relax config file syntax checking to allow directives for future OpenVPN versions to be ignored. --ignore-unkown-option opt1 opt2 ...: Relax config file syntax. Allow these options to be ignored when unknown --script-security level: Where level can be: 0 -- strictly no calling of external programs 1 -- (default) only call built-ins such as ifconfig 2 -- allow calling of built-ins and scripts 3 -- allow password to be passed to scripts via env --shaper n : Restrict output to peer to n bytes per second. --keepalive n m : Helper option for setting timeouts in server mode. Send ping once every n seconds, restart if ping not received for m seconds. --inactive n [bytes] : Exit after n seconds of activity on tun/tap device produces a combined in/out byte count < bytes. --ping-exit n : Exit if n seconds pass without reception of remote ping. --ping-restart n: Restart if n seconds pass without reception of remote ping. --ping-timer-rem: Run the --ping-exit/--ping-restart timer only if we have a remote address. --ping n : Ping remote once every n seconds over TCP/UDP port. --multihome : Configure a multi-homed UDP server. --fast-io : (experimental) Optimize TUN/TAP/UDP writes. --remap-usr1 s : On SIGUSR1 signals, remap signal (s='SIGHUP' or 'SIGTERM'). --persist-tun : Keep tun/tap device open across SIGUSR1 or --ping-restart. --persist-remote-ip : Keep remote IP address across SIGUSR1 or --ping-restart. --persist-local-ip : Keep local IP address across SIGUSR1 or --ping-restart. --persist-key : Don't re-read key files across SIGUSR1 or --ping-restart. --passtos : TOS passthrough (applies to IPv4 only). --tun-mtu n : Take the tun/tap device MTU to be n and derive the TCP/UDP MTU from it (default=1500). --tun-mtu-extra n : Assume that tun/tap device might return as many as n bytes more than the tun-mtu size on read (default TUN=0 TAP=32). --link-mtu n : Take the TCP/UDP device MTU to be n and derive the tun MTU from it. --mtu-disc type : Should we do Path MTU discovery on TCP/UDP channel? 'no' -- Never send DF (Don't Fragment) frames 'maybe' -- Use per-route hints 'yes' -- Always DF (Don't Fragment) --mtu-test : Empirically measure and report MTU. --fragment max : Enable internal datagram fragmentation so that no UDP datagrams are sent which are larger than max bytes. Adds 4 bytes of overhead per datagram. --mssfix [n] : Set upper bound on TCP MSS, default = tun-mtu size or --fragment max value, whichever is lower. --sndbuf size : Set the TCP/UDP send buffer size. --rcvbuf size : Set the TCP/UDP receive buffer size. --mark value : Mark encrypted packets being sent with value. The mark value can be matched in policy routing and packetfilter rules. --bind-dev dev : Bind to the given device when making connection to a peer or listening for connections. This allows sending encrypted packets via a VRF present on the system. --txqueuelen n : Set the tun/tap TX queue length to n (Linux only). --memstats file : Write live usage stats to memory mapped binary file. --mlock : Disable Paging -- ensures key material and tunnel data will never be written to disk. --up cmd : Run command cmd after successful tun device open. Execute as: cmd tun/tap-dev tun-mtu link-mtu \ ifconfig-local-ip ifconfig-remote-ip (pre --user or --group UID/GID change) --up-delay : Delay tun/tap open and possible --up script execution until after TCP/UDP connection establishment with peer. --down cmd : Run command cmd after tun device close. (post --user/--group UID/GID change and/or --chroot) (command parameters are same as --up option) --down-pre : Run --down command before TUN/TAP close. --up-restart : Run up/down commands for all restarts including those caused by --ping-restart or SIGUSR1 --user user : Set UID to user after initialization. --group group : Set GID to group after initialization. --chroot dir : Chroot to this directory after initialization. --cd dir : Change to this directory before initialization. --daemon [name] : Become a daemon after initialization. The optional 'name' parameter will be passed as the program name to the system logger. --syslog [name] : Output to syslog, but do not become a daemon. See --daemon above for a description of the 'name' parm. --inetd [name] ['wait'|'nowait'] : Run as an inetd or xinetd server. See --daemon above for a description of the 'name' parm. --log file : Output log to file which is created/truncated on open. --log-append file : Append log to file, or create file if nonexistent. --suppress-timestamps : Don't log timestamps to stdout/stderr. --machine-readable-output : Always log timestamp, message flags to stdout/stderr. --writepid file : Write main process ID to file. --nice n : Change process priority (>0 = lower, <0 = higher). --echo [parms ...] : Echo parameters to log output. --verb n : Set output verbosity to n (default=1): (Level 3 is recommended if you want a good summary of what's happening without being swamped by output). : 0 -- no output except fatal errors : 1 -- startup info + connection initiated messages + non-fatal encryption & net errors : 2,3 -- show TLS negotiations & route info : 4 -- show parameters : 5 -- show 'RrWw' chars on console for each packet sent and received from TCP/UDP (caps) or tun/tap (lc) : 6 to 11 -- debug messages of increasing verbosity --mute n : Log at most n consecutive messages in the same category. --status file n : Write operational status to file every n seconds. --status-version [n] : Choose the status file format version number. Currently, n can be 1, 2, or 3 (default=1). --disable-occ : Disable options consistency check between peers. --gremlin mask : Special stress testing mode (for debugging only). --compress alg : Use compression algorithm alg --allow-compression: Specify whether compression should be allowed --comp-lzo : Use LZO compression -- may add up to 1 byte per packet for incompressible data. --comp-noadapt : Don't use adaptive compression when --comp-lzo is specified. --management ip port [pass] : Enable a TCP server on ip:port to handle management functions. pass is a password file or 'stdin' to prompt from console. To listen on a unix domain socket, specific the pathname in place of ip and use 'unix' as the port number. --management-client : Management interface will connect as a TCP client to ip/port rather than listen as a TCP server. --management-query-passwords : Query management channel for private key and auth-user-pass passwords. --management-query-proxy : Query management channel for proxy information. --management-query-remote : Query management channel for --remote directive. --management-hold : Start OpenVPN in a hibernating state, until a client of the management interface explicitly starts it. --management-signal : Issue SIGUSR1 when management disconnect event occurs. --management-forget-disconnect : Forget passwords when management disconnect event occurs. --management-up-down : Report tunnel up/down events to management interface. --management-log-cache n : Cache n lines of log file history for usage by the management channel. --management-client-user u : When management interface is a unix socket, only allow connections from user u. --management-client-group g : When management interface is a unix socket, only allow connections from group g. --management-client-auth : gives management interface client the responsibility to authenticate clients after their client certificate has been verified. --management-client-pf : management interface clients must specify a packet filter file for each connecting client. --plugin m [str]: Load plug-in module m passing str as an argument to its initialization function. --vlan-tagging : Enable 802.1Q-based VLAN tagging. --vlan-accept tagged|untagged|all : Set VLAN tagging mode. Default is 'all'. --vlan-pvid v : Sets the Port VLAN Identifier. Defaults to 1. Multi-Client Server options (when --mode server is used): --server network netmask : Helper option to easily configure server mode. --server-ipv6 network/bits : Configure IPv6 server mode. --server-bridge [IP netmask pool-start-IP pool-end-IP] : Helper option to easily configure ethernet bridging server mode. --push "option" : Push a config file option back to the peer for remote execution. Peer must specify --pull in its config file. --push-reset : Don't inherit global push list for specific client instance. --push-remove opt : Remove options matching 'opt' from the push list for a specific client instance. --ifconfig-pool start-IP end-IP [netmask] : Set aside a pool of subnets to be dynamically allocated to connecting clients. --ifconfig-pool-persist file [seconds] : Persist/unpersist ifconfig-pool data to file, at seconds intervals (default=600). If seconds=0, file will be treated as read-only. --ifconfig-ipv6-pool base-IP/bits : set aside an IPv6 network block to be dynamically allocated to connecting clients. --ifconfig-push local remote-netmask : Push an ifconfig option to remote, overrides --ifconfig-pool dynamic allocation. Only valid in a client-specific config file. --ifconfig-ipv6-push local/bits remote : Push an ifconfig-ipv6 option to remote, overrides --ifconfig-ipv6-pool allocation. Only valid in a client-specific config file. --iroute network [netmask] : Route subnet to client. --iroute-ipv6 network/bits : Route IPv6 subnet to client. Sets up internal routes only. Only valid in a client-specific config file. --disable : Client is disabled. Only valid in a client-specific config file. --verify-client-cert [none|optional|require] : perform no, optional or mandatory client certificate verification. Default is to require the client to supply a certificate. --username-as-common-name : For auth-user-pass authentication, use the authenticated username as the common name, rather than the common name from the client cert. --auth-user-pass-verify cmd method: Query client for username/password and run command cmd to verify. If method='via-env', pass user/pass via environment, if method='via-file', pass user/pass via temporary file. --auth-gen-token [lifetime] Generate a random authentication token which is pushed to each client, replacing the password. Useful when OTP based two-factor auth mechanisms are in use and --reneg-* options are enabled. Optionally a lifetime in seconds for generated tokens can be set. --opt-verify : Clients that connect with options that are incompatible with those of the server will be disconnected. --auth-user-pass-optional : Allow connections by clients that don't specify a username/password. --no-name-remapping : (DEPRECATED) Allow Common Name and X509 Subject to include any printable character. --client-to-client : Internally route client-to-client traffic. --duplicate-cn : Allow multiple clients with the same common name to concurrently connect. --client-connect cmd : Run command cmd on client connection. --client-disconnect cmd : Run command cmd on client disconnection. --client-config-dir dir : Directory for custom client config files. --ccd-exclusive : Refuse connection unless custom client config is found. --tmp-dir dir : Temporary directory, used for --client-connect return file and plugin communication. --hash-size r v : Set the size of the real address hash table to r and the virtual address table to v. --bcast-buffers n : Allocate n broadcast buffers. --tcp-queue-limit n : Maximum number of queued TCP output packets. --tcp-nodelay : Macro that sets TCP_NODELAY socket flag on the server as well as pushes it to connecting clients. --learn-address cmd : Run command cmd to validate client virtual addresses. --connect-freq n s : Allow a maximum of n new connections per s seconds. --max-clients n : Allow a maximum of n simultaneously connected clients. --max-routes-per-client n : Allow a maximum of n internal routes per client. --stale-routes-check n [t] : Remove routes with a last activity timestamp older than n seconds. Run this check every t seconds (defaults to n). --explicit-exit-notify [n] : In UDP server mode send [RESTART] command on exit/restart to connected clients. n = 1 - reconnect to same server, 2 - advance to next server, default=1. --port-share host port [dir] : When run in TCP mode, proxy incoming HTTPS sessions to a web server at host:port. dir specifies an optional directory to write origin IP:port data. Client options (when connecting to a multi-client server): --client : Helper option to easily configure client mode. --auth-user-pass [up] : Authenticate with server using username/password. up is a file containing the username on the first line, and a password on the second. If either the password or both the username and the password are omitted OpenVPN will prompt for them from console. --pull : Accept certain config file options from the peer as if they were part of the local config file. Must be specified when connecting to a '--mode server' remote host. --pull-filter accept|ignore|reject t : Filter each option received from the server if it starts with the text t. The action flag accept, ignore or reject causes the option to be allowed, removed or rejected with error. May be specified multiple times, and each filter is applied in the order of appearance. --auth-retry t : How to handle auth failures. Set t to none (default), interact, or nointeract. --static-challenge t e : Enable static challenge/response protocol using challenge text t, with e indicating echo flag (0|1) --connect-timeout n : when polling possible remote servers to connect to in a round-robin fashion, spend no more than n seconds waiting for a response before trying the next server. --allow-recursive-routing : When this option is set, OpenVPN will not drop incoming tun packets with same destination as host. --explicit-exit-notify [n] : On exit/restart, send exit signal to server/remote. n = # of retries, default=1. Data Channel Encryption Options (must be compatible between peers): (These options are meaningful for both Static Key & TLS-mode) --secret f [d] : Enable Static Key encryption mode (non-TLS). Use shared secret file f, generate with --genkey. The optional d parameter controls key directionality. If d is specified, use separate keys for each direction, set d=0 on one side of the connection, and d=1 on the other side. --auth alg : Authenticate packets with HMAC using message digest algorithm alg (default=SHA1). (usually adds 16 or 20 bytes per packet) Set alg=none to disable authentication. --cipher alg : Encrypt packets with cipher algorithm alg (default=(null)). Set alg=none to disable encryption. --data-ciphers list : List of ciphers that are allowed to be negotiated. --ncp-disable : (DEPRECATED) Disable cipher negotiation. --prng alg [nsl] : For PRNG, use digest algorithm alg, and nonce_secret_len=nsl. Set alg=none to disable PRNG. --keysize n : (DEPRECATED) Size of cipher key in bits (optional). If unspecified, defaults to cipher-specific default. --engine [name] : Enable OpenSSL hardware crypto engine functionality. --no-replay : (DEPRECATED) Disable replay protection. --mute-replay-warnings : Silence the output of replay warnings to log file. --replay-window n [t] : Use a replay protection sliding window of size n and a time window of t seconds. Default n=64 t=15 --replay-persist file : Persist replay-protection state across sessions using file. --test-crypto : Run a self-test of crypto features enabled. For debugging only. TLS Key Negotiation Options: (These options are meaningful only for TLS-mode) --tls-server : Enable TLS and assume server role during TLS handshake. --tls-client : Enable TLS and assume client role during TLS handshake. --key-method m : (DEPRECATED) Data channel key exchange method. m should be a method number, such as 1 (default), 2, etc. --ca file : Certificate authority file in .pem format containing root certificate. --capath dir : A directory of trusted certificates (CAs and CRLs). --dh file : File containing Diffie Hellman parameters in .pem format (for --tls-server only). Use "openssl dhparam -out dh1024.pem 1024" to generate. --cert file : Local certificate in .pem format -- must be signed by a Certificate Authority in --ca file. --extra-certs file : one or more PEM certs that complete the cert chain. --key file : Local private key in .pem format. --tls-version-min <version> ['or-highest'] : sets the minimum TLS version we will accept from the peer. If version is unrecognized and 'or-highest' is specified, require max TLS version supported by SSL implementation. --tls-version-max <version> : sets the maximum TLS version we will use. --pkcs12 file : PKCS#12 file containing local private key, local certificate and optionally the root CA certificate. --x509-username-field : Field in x509 certificate containing the username. Default is CN in the Subject field. --verify-hash hash [algo] : Specify fingerprint for level-1 certificate. Valid algo flags are SHA1 and SHA256. --tls-cipher l : A list l of allowable TLS ciphers separated by : (optional). --tls-ciphersuites l: A list of allowed TLS 1.3 cipher suites seperated by : (optional) : Use --show-tls to see a list of supported TLS ciphers (suites). --tls-cert-profile p : Set the allowed certificate crypto algorithm profile (default=legacy). --tls-timeout n : Packet retransmit timeout on TLS control channel if no ACK from remote within n seconds (default=2). --reneg-bytes n : Renegotiate data chan. key after n bytes sent and recvd. --reneg-pkts n : Renegotiate data chan. key after n packets sent and recvd. --reneg-sec max [min] : Renegotiate data chan. key after at most max (default=3600) and at least min (defaults to 90% of max on servers and equal to max on clients). --hand-window n : Data channel key exchange must finalize within n seconds of handshake initiation by any peer (default=60). --tran-window n : Transition window -- old key can live this many seconds after new key renegotiation begins (default=3600). --single-session: Allow only one session (reset state on restart). --tls-exit : Exit on TLS negotiation failure. --tls-auth f [d]: Add an additional layer of authentication on top of the TLS control channel to protect against attacks on the TLS stack and DoS attacks. f (required) is a shared-secret key file. The optional d parameter controls key directionality, see --secret option for more info. --tls-crypt key : Add an additional layer of authenticated encryption on top of the TLS control channel to hide the TLS certificate, provide basic post-quantum security and protect against attacks on the TLS stack and DoS attacks. key (required) provides the pre-shared key file. see --secret option for more info. --tls-crypt-v2 key : For clients: use key as a client-specific tls-crypt key. For servers: use key to decrypt client-specific keys. For key generation (--genkey tls-crypt-v2-client): use key to encrypt generated client-specific key. (See --tls-crypt.) --genkey tls-crypt-v2-client [keyfile] [base64 metadata]: Generate a fresh tls-crypt-v2 client key, and store to keyfile. If supplied, include metadata in wrapped key. --genkey tls-crypt-v2-server [keyfile] [base64 metadata]: Generate a fresh tls-crypt-v2 server key, and store to keyfile --tls-crypt-v2-verify cmd : Run command cmd to verify the metadata of the client-supplied tls-crypt-v2 client key --askpass [file]: Get PEM password from controlling tty before we daemonize. --auth-nocache : Don't cache --askpass or --auth-user-pass passwords. --crl-verify crl ['dir']: Check peer certificate against a CRL. --tls-verify cmd: Run command cmd to verify the X509 name of a pending TLS connection that has otherwise passed all other tests of certification. cmd should return 0 to allow TLS handshake to proceed, or 1 to fail. (cmd is executed as 'cmd certificate_depth subject') --tls-export-cert [directory] : Get peer cert in PEM format and store it in an openvpn temporary file in [directory]. Peer cert is stored before tls-verify script execution and deleted after. --verify-x509-name name: Accept connections only from a host with X509 subject DN name. The remote host must also pass all other tests of verification. --ns-cert-type t: (DEPRECATED) Require that peer certificate was signed with an explicit nsCertType designation t = 'client' | 'server'. --x509-track x : Save peer X509 attribute x in environment for use by plugins and management interface. --keying-material-exporter label len : Save Exported Keying Material (RFC5705) of len bytes (min. 16 bytes) using label in environment for use by plugins. --remote-cert-ku v ... : Require that the peer certificate was signed with explicit key usage, you can specify more than one value. value should be given in hex format. --remote-cert-eku oid : Require that the peer certificate was signed with explicit extended key usage. Extended key usage can be encoded as an object identifier or OpenSSL string representation. --remote-cert-tls t: Require that peer certificate was signed with explicit key usage and extended key usage based on RFC3280 TLS rules. t = 'client' | 'server'. PKCS#11 Options: --pkcs11-providers provider ... : PKCS#11 provider to load. --pkcs11-protected-authentication [0|1] ... : Use PKCS#11 protected authentication path. Set for each provider. --pkcs11-private-mode hex ... : PKCS#11 private key mode mask. 0 : Try to determine automatically (default). 1 : Use Sign. 2 : Use SignRecover. 4 : Use Decrypt. 8 : Use Unwrap. --pkcs11-cert-private [0|1] ... : Set if login should be performed before certificate can be accessed. Set for each provider. --pkcs11-pin-cache seconds : Number of seconds to cache PIN. The default is -1 cache until token is removed. --pkcs11-id-management : Acquire identity from management interface. --pkcs11-id serialized-id 'id' : Identity to use, get using standalone --show-pkcs11-ids SSL Library information: --show-ciphers : Show cipher algorithms to use with --cipher option. --show-digests : Show message digest algorithms to use with --auth option. --show-engines : Show hardware crypto accelerator engines (if available). --show-tls : Show all TLS ciphers (TLS used only as a control channel). Generate a new key : --genkey secret file : Generate a new random key of type and write to file (for use with --secret, --tls-auth or --tls-crypt). Tun/tap config mode (available with linux 2.4+): --mktun : Create a persistent tunnel. --rmtun : Remove a persistent tunnel. --dev tunX|tapX : tun/tap device --dev-type dt : Device type. See tunnel options above for details. --user user : User to set privilege to. --group group : Group to set privilege to. PKCS#11 standalone options: --show-pkcs11-ids [provider] [cert_private] : Show PKCS#11 available ids. --verb option can be added *BEFORE* this. General Standalone Options: --show-gateway : Show info about default gateway.二、启动命令sudo nohup openvpn VPNConfig.ovpn > /dev/null &三、关闭命令myserver@DESKTOP-QNAP:~/programs/soft/openvpn$ ps -ef|grep openvpn root 600136 1 0 5月22 ? 00:00:00 sudo nohup openvpn VPNConfig.ovpn root 600137 600136 0 5月22 pts/1 00:00:00 sudo nohup openvpn VPNConfig.ovpn root 600138 600137 0 5月22 pts/1 00:00:10 openvpn VPNConfig.ovpn myserver 3227085 3221195 0 00:00 pts/2 00:00:00 grep --color=auto openvpn myserver@DESKTOP-QNAP:~/programs/soft/openvpn$ kill -9 600136
OpenVPN在linux中的命令 一、配置项OpenVPN 2.5.5 x86_64-pc-linux-gnu [SSL (OpenSSL)] [LZO] [LZ4] [EPOLL] [PKCS11] [MH/PKTINFO] [AEAD] built on Mar 22 2022 General Options: --config file : Read configuration options from file. --help : Show options. --version : Show copyright and version information. Tunnel Options: --local host : Local host name or ip address. Implies --bind. --remote host [port] : Remote host name or ip address. --remote-random : If multiple --remote options specified, choose one randomly. --remote-random-hostname : Add a random string to remote DNS name. --mode m : Major mode, m = 'p2p' (default, point-to-point) or 'server'. --proto p : Use protocol p for communicating with peer. p = udp (default), tcp-server, or tcp-client --proto-force p : only consider protocol p in list of connection profiles. p = udp6, tcp6-server, or tcp6-client (ipv6) --connect-retry n [m] : For client, number of seconds to wait between connection retries (default=5). On repeated retries the wait time is exponentially increased to a maximum of m (default=300). --connect-retry-max n : Maximum connection attempt retries, default infinite. --http-proxy s p [up] [auth] : Connect to remote host through an HTTP proxy at address s and port p. If proxy authentication is required, up is a file containing username/password on 2 lines, or 'stdin' to prompt from console. Add auth='ntlm' if the proxy requires NTLM authentication. --http-proxy s p 'auto[-nct]' : Like the above directive, but automatically determine auth method and query for username/password if needed. auto-nct disables weak proxy auth methods. --http-proxy-option type [parm] : Set extended HTTP proxy options. Repeat to set multiple options. VERSION version (default=1.0) AGENT user-agent --socks-proxy s [p] [up] : Connect to remote host through a Socks5 proxy at address s and port p (default port = 1080). If proxy authentication is required, up is a file containing username/password on 2 lines, or 'stdin' to prompt for console. --socks-proxy-retry : Retry indefinitely on Socks proxy errors. --resolv-retry n: If hostname resolve fails for --remote, retry resolve for n seconds before failing (disabled by default). Set n="infinite" to retry indefinitely. --float : Allow remote to change its IP address/port, such as through DHCP (this is the default if --remote is not used). --ipchange cmd : Run command cmd on remote ip address initial setting or change -- execute as: cmd ip-address port# --port port : TCP/UDP port # for both local and remote. --lport port : TCP/UDP port # for local (default=1194). Implies --bind. --rport port : TCP/UDP port # for remote (default=1194). --bind : Bind to local address and port. (This is the default unless --proto tcp-client or --http-proxy or --socks-proxy is used). --nobind : Do not bind to local address and port. --dev tunX|tapX : tun/tap device (X can be omitted for dynamic device. --dev-type dt : Which device type are we using? (dt = tun or tap) Use this option only if the tun/tap device used with --dev does not begin with "tun" or "tap". --dev-node node : Explicitly set the device node rather than using /dev/net/tun, /dev/tun, /dev/tap, etc. --lladdr hw : Set the link layer address of the tap device. --topology t : Set --dev tun topology: 'net30', 'p2p', or 'subnet'. --ifconfig l rn : TUN: configure device to use IP address l as a local endpoint and rn as a remote endpoint. l & rn should be swapped on the other peer. l & rn must be private addresses outside of the subnets used by either peer. TAP: configure device to use IP address l as a local endpoint and rn as a subnet mask. --ifconfig-ipv6 l r : configure device to use IPv6 address l as local endpoint (as a /64) and r as remote endpoint --ifconfig-noexec : Don't actually execute ifconfig/netsh command, instead pass --ifconfig parms by environment to scripts. --ifconfig-nowarn : Don't warn if the --ifconfig option on this side of the connection doesn't match the remote side. --route network [netmask] [gateway] [metric] : Add route to routing table after connection is established. Multiple routes can be specified. netmask default: 255.255.255.255 gateway default: taken from --route-gateway or --ifconfig Specify default by leaving blank or setting to "default". --route-ipv6 network/bits [gateway] [metric] : Add IPv6 route to routing table after connection is established. Multiple routes can be specified. gateway default: taken from --route-ipv6-gateway or 'remote' in --ifconfig-ipv6 --route-gateway gw|'dhcp' : Specify a default gateway for use with --route. --route-ipv6-gateway gw : Specify a default gateway for use with --route-ipv6. --route-metric m : Specify a default metric for use with --route. --route-delay n [w] : Delay n seconds after connection initiation before adding routes (may be 0). If not specified, routes will be added immediately after tun/tap open. On Windows, wait up to w seconds for TUN/TAP adapter to come up. --route-up cmd : Run command cmd after routes are added. --route-pre-down cmd : Run command cmd before routes are removed. --route-noexec : Don't add routes automatically. Instead pass routes to --route-up script using environmental variables. --route-nopull : When used with --client or --pull, accept options pushed by server EXCEPT for routes and dhcp options. --allow-pull-fqdn : Allow client to pull DNS names from server for --ifconfig, --route, and --route-gateway. --redirect-gateway [flags]: Automatically execute routing commands to redirect all outgoing IP traffic through the VPN. Add 'local' flag if both OpenVPN servers are directly connected via a common subnet, such as with WiFi. Add 'def1' flag to set default route using using 0.0.0.0/1 and 128.0.0.0/1 rather than 0.0.0.0/0. Add 'bypass-dhcp' flag to add a direct route to DHCP server, bypassing tunnel. Add 'bypass-dns' flag to similarly bypass tunnel for DNS. --redirect-private [flags]: Like --redirect-gateway, but omit actually changing the default gateway. Useful when pushing private subnets. --block-ipv6 : (Client) Instead sending IPv6 to the server generate ICMPv6 host unreachable messages on the client. (Server) Instead of forwarding IPv6 packets send ICMPv6 host unreachable packets to the client. --client-nat snat|dnat network netmask alias : on client add 1-to-1 NAT rule. --push-peer-info : (client only) push client info to server. --setenv name value : Set a custom environmental variable to pass to script. --setenv FORWARD_COMPATIBLE 1 : Relax config file syntax checking to allow directives for future OpenVPN versions to be ignored. --ignore-unkown-option opt1 opt2 ...: Relax config file syntax. Allow these options to be ignored when unknown --script-security level: Where level can be: 0 -- strictly no calling of external programs 1 -- (default) only call built-ins such as ifconfig 2 -- allow calling of built-ins and scripts 3 -- allow password to be passed to scripts via env --shaper n : Restrict output to peer to n bytes per second. --keepalive n m : Helper option for setting timeouts in server mode. Send ping once every n seconds, restart if ping not received for m seconds. --inactive n [bytes] : Exit after n seconds of activity on tun/tap device produces a combined in/out byte count < bytes. --ping-exit n : Exit if n seconds pass without reception of remote ping. --ping-restart n: Restart if n seconds pass without reception of remote ping. --ping-timer-rem: Run the --ping-exit/--ping-restart timer only if we have a remote address. --ping n : Ping remote once every n seconds over TCP/UDP port. --multihome : Configure a multi-homed UDP server. --fast-io : (experimental) Optimize TUN/TAP/UDP writes. --remap-usr1 s : On SIGUSR1 signals, remap signal (s='SIGHUP' or 'SIGTERM'). --persist-tun : Keep tun/tap device open across SIGUSR1 or --ping-restart. --persist-remote-ip : Keep remote IP address across SIGUSR1 or --ping-restart. --persist-local-ip : Keep local IP address across SIGUSR1 or --ping-restart. --persist-key : Don't re-read key files across SIGUSR1 or --ping-restart. --passtos : TOS passthrough (applies to IPv4 only). --tun-mtu n : Take the tun/tap device MTU to be n and derive the TCP/UDP MTU from it (default=1500). --tun-mtu-extra n : Assume that tun/tap device might return as many as n bytes more than the tun-mtu size on read (default TUN=0 TAP=32). --link-mtu n : Take the TCP/UDP device MTU to be n and derive the tun MTU from it. --mtu-disc type : Should we do Path MTU discovery on TCP/UDP channel? 'no' -- Never send DF (Don't Fragment) frames 'maybe' -- Use per-route hints 'yes' -- Always DF (Don't Fragment) --mtu-test : Empirically measure and report MTU. --fragment max : Enable internal datagram fragmentation so that no UDP datagrams are sent which are larger than max bytes. Adds 4 bytes of overhead per datagram. --mssfix [n] : Set upper bound on TCP MSS, default = tun-mtu size or --fragment max value, whichever is lower. --sndbuf size : Set the TCP/UDP send buffer size. --rcvbuf size : Set the TCP/UDP receive buffer size. --mark value : Mark encrypted packets being sent with value. The mark value can be matched in policy routing and packetfilter rules. --bind-dev dev : Bind to the given device when making connection to a peer or listening for connections. This allows sending encrypted packets via a VRF present on the system. --txqueuelen n : Set the tun/tap TX queue length to n (Linux only). --memstats file : Write live usage stats to memory mapped binary file. --mlock : Disable Paging -- ensures key material and tunnel data will never be written to disk. --up cmd : Run command cmd after successful tun device open. Execute as: cmd tun/tap-dev tun-mtu link-mtu \ ifconfig-local-ip ifconfig-remote-ip (pre --user or --group UID/GID change) --up-delay : Delay tun/tap open and possible --up script execution until after TCP/UDP connection establishment with peer. --down cmd : Run command cmd after tun device close. (post --user/--group UID/GID change and/or --chroot) (command parameters are same as --up option) --down-pre : Run --down command before TUN/TAP close. --up-restart : Run up/down commands for all restarts including those caused by --ping-restart or SIGUSR1 --user user : Set UID to user after initialization. --group group : Set GID to group after initialization. --chroot dir : Chroot to this directory after initialization. --cd dir : Change to this directory before initialization. --daemon [name] : Become a daemon after initialization. The optional 'name' parameter will be passed as the program name to the system logger. --syslog [name] : Output to syslog, but do not become a daemon. See --daemon above for a description of the 'name' parm. --inetd [name] ['wait'|'nowait'] : Run as an inetd or xinetd server. See --daemon above for a description of the 'name' parm. --log file : Output log to file which is created/truncated on open. --log-append file : Append log to file, or create file if nonexistent. --suppress-timestamps : Don't log timestamps to stdout/stderr. --machine-readable-output : Always log timestamp, message flags to stdout/stderr. --writepid file : Write main process ID to file. --nice n : Change process priority (>0 = lower, <0 = higher). --echo [parms ...] : Echo parameters to log output. --verb n : Set output verbosity to n (default=1): (Level 3 is recommended if you want a good summary of what's happening without being swamped by output). : 0 -- no output except fatal errors : 1 -- startup info + connection initiated messages + non-fatal encryption & net errors : 2,3 -- show TLS negotiations & route info : 4 -- show parameters : 5 -- show 'RrWw' chars on console for each packet sent and received from TCP/UDP (caps) or tun/tap (lc) : 6 to 11 -- debug messages of increasing verbosity --mute n : Log at most n consecutive messages in the same category. --status file n : Write operational status to file every n seconds. --status-version [n] : Choose the status file format version number. Currently, n can be 1, 2, or 3 (default=1). --disable-occ : Disable options consistency check between peers. --gremlin mask : Special stress testing mode (for debugging only). --compress alg : Use compression algorithm alg --allow-compression: Specify whether compression should be allowed --comp-lzo : Use LZO compression -- may add up to 1 byte per packet for incompressible data. --comp-noadapt : Don't use adaptive compression when --comp-lzo is specified. --management ip port [pass] : Enable a TCP server on ip:port to handle management functions. pass is a password file or 'stdin' to prompt from console. To listen on a unix domain socket, specific the pathname in place of ip and use 'unix' as the port number. --management-client : Management interface will connect as a TCP client to ip/port rather than listen as a TCP server. --management-query-passwords : Query management channel for private key and auth-user-pass passwords. --management-query-proxy : Query management channel for proxy information. --management-query-remote : Query management channel for --remote directive. --management-hold : Start OpenVPN in a hibernating state, until a client of the management interface explicitly starts it. --management-signal : Issue SIGUSR1 when management disconnect event occurs. --management-forget-disconnect : Forget passwords when management disconnect event occurs. --management-up-down : Report tunnel up/down events to management interface. --management-log-cache n : Cache n lines of log file history for usage by the management channel. --management-client-user u : When management interface is a unix socket, only allow connections from user u. --management-client-group g : When management interface is a unix socket, only allow connections from group g. --management-client-auth : gives management interface client the responsibility to authenticate clients after their client certificate has been verified. --management-client-pf : management interface clients must specify a packet filter file for each connecting client. --plugin m [str]: Load plug-in module m passing str as an argument to its initialization function. --vlan-tagging : Enable 802.1Q-based VLAN tagging. --vlan-accept tagged|untagged|all : Set VLAN tagging mode. Default is 'all'. --vlan-pvid v : Sets the Port VLAN Identifier. Defaults to 1. Multi-Client Server options (when --mode server is used): --server network netmask : Helper option to easily configure server mode. --server-ipv6 network/bits : Configure IPv6 server mode. --server-bridge [IP netmask pool-start-IP pool-end-IP] : Helper option to easily configure ethernet bridging server mode. --push "option" : Push a config file option back to the peer for remote execution. Peer must specify --pull in its config file. --push-reset : Don't inherit global push list for specific client instance. --push-remove opt : Remove options matching 'opt' from the push list for a specific client instance. --ifconfig-pool start-IP end-IP [netmask] : Set aside a pool of subnets to be dynamically allocated to connecting clients. --ifconfig-pool-persist file [seconds] : Persist/unpersist ifconfig-pool data to file, at seconds intervals (default=600). If seconds=0, file will be treated as read-only. --ifconfig-ipv6-pool base-IP/bits : set aside an IPv6 network block to be dynamically allocated to connecting clients. --ifconfig-push local remote-netmask : Push an ifconfig option to remote, overrides --ifconfig-pool dynamic allocation. Only valid in a client-specific config file. --ifconfig-ipv6-push local/bits remote : Push an ifconfig-ipv6 option to remote, overrides --ifconfig-ipv6-pool allocation. Only valid in a client-specific config file. --iroute network [netmask] : Route subnet to client. --iroute-ipv6 network/bits : Route IPv6 subnet to client. Sets up internal routes only. Only valid in a client-specific config file. --disable : Client is disabled. Only valid in a client-specific config file. --verify-client-cert [none|optional|require] : perform no, optional or mandatory client certificate verification. Default is to require the client to supply a certificate. --username-as-common-name : For auth-user-pass authentication, use the authenticated username as the common name, rather than the common name from the client cert. --auth-user-pass-verify cmd method: Query client for username/password and run command cmd to verify. If method='via-env', pass user/pass via environment, if method='via-file', pass user/pass via temporary file. --auth-gen-token [lifetime] Generate a random authentication token which is pushed to each client, replacing the password. Useful when OTP based two-factor auth mechanisms are in use and --reneg-* options are enabled. Optionally a lifetime in seconds for generated tokens can be set. --opt-verify : Clients that connect with options that are incompatible with those of the server will be disconnected. --auth-user-pass-optional : Allow connections by clients that don't specify a username/password. --no-name-remapping : (DEPRECATED) Allow Common Name and X509 Subject to include any printable character. --client-to-client : Internally route client-to-client traffic. --duplicate-cn : Allow multiple clients with the same common name to concurrently connect. --client-connect cmd : Run command cmd on client connection. --client-disconnect cmd : Run command cmd on client disconnection. --client-config-dir dir : Directory for custom client config files. --ccd-exclusive : Refuse connection unless custom client config is found. --tmp-dir dir : Temporary directory, used for --client-connect return file and plugin communication. --hash-size r v : Set the size of the real address hash table to r and the virtual address table to v. --bcast-buffers n : Allocate n broadcast buffers. --tcp-queue-limit n : Maximum number of queued TCP output packets. --tcp-nodelay : Macro that sets TCP_NODELAY socket flag on the server as well as pushes it to connecting clients. --learn-address cmd : Run command cmd to validate client virtual addresses. --connect-freq n s : Allow a maximum of n new connections per s seconds. --max-clients n : Allow a maximum of n simultaneously connected clients. --max-routes-per-client n : Allow a maximum of n internal routes per client. --stale-routes-check n [t] : Remove routes with a last activity timestamp older than n seconds. Run this check every t seconds (defaults to n). --explicit-exit-notify [n] : In UDP server mode send [RESTART] command on exit/restart to connected clients. n = 1 - reconnect to same server, 2 - advance to next server, default=1. --port-share host port [dir] : When run in TCP mode, proxy incoming HTTPS sessions to a web server at host:port. dir specifies an optional directory to write origin IP:port data. Client options (when connecting to a multi-client server): --client : Helper option to easily configure client mode. --auth-user-pass [up] : Authenticate with server using username/password. up is a file containing the username on the first line, and a password on the second. If either the password or both the username and the password are omitted OpenVPN will prompt for them from console. --pull : Accept certain config file options from the peer as if they were part of the local config file. Must be specified when connecting to a '--mode server' remote host. --pull-filter accept|ignore|reject t : Filter each option received from the server if it starts with the text t. The action flag accept, ignore or reject causes the option to be allowed, removed or rejected with error. May be specified multiple times, and each filter is applied in the order of appearance. --auth-retry t : How to handle auth failures. Set t to none (default), interact, or nointeract. --static-challenge t e : Enable static challenge/response protocol using challenge text t, with e indicating echo flag (0|1) --connect-timeout n : when polling possible remote servers to connect to in a round-robin fashion, spend no more than n seconds waiting for a response before trying the next server. --allow-recursive-routing : When this option is set, OpenVPN will not drop incoming tun packets with same destination as host. --explicit-exit-notify [n] : On exit/restart, send exit signal to server/remote. n = # of retries, default=1. Data Channel Encryption Options (must be compatible between peers): (These options are meaningful for both Static Key & TLS-mode) --secret f [d] : Enable Static Key encryption mode (non-TLS). Use shared secret file f, generate with --genkey. The optional d parameter controls key directionality. If d is specified, use separate keys for each direction, set d=0 on one side of the connection, and d=1 on the other side. --auth alg : Authenticate packets with HMAC using message digest algorithm alg (default=SHA1). (usually adds 16 or 20 bytes per packet) Set alg=none to disable authentication. --cipher alg : Encrypt packets with cipher algorithm alg (default=(null)). Set alg=none to disable encryption. --data-ciphers list : List of ciphers that are allowed to be negotiated. --ncp-disable : (DEPRECATED) Disable cipher negotiation. --prng alg [nsl] : For PRNG, use digest algorithm alg, and nonce_secret_len=nsl. Set alg=none to disable PRNG. --keysize n : (DEPRECATED) Size of cipher key in bits (optional). If unspecified, defaults to cipher-specific default. --engine [name] : Enable OpenSSL hardware crypto engine functionality. --no-replay : (DEPRECATED) Disable replay protection. --mute-replay-warnings : Silence the output of replay warnings to log file. --replay-window n [t] : Use a replay protection sliding window of size n and a time window of t seconds. Default n=64 t=15 --replay-persist file : Persist replay-protection state across sessions using file. --test-crypto : Run a self-test of crypto features enabled. For debugging only. TLS Key Negotiation Options: (These options are meaningful only for TLS-mode) --tls-server : Enable TLS and assume server role during TLS handshake. --tls-client : Enable TLS and assume client role during TLS handshake. --key-method m : (DEPRECATED) Data channel key exchange method. m should be a method number, such as 1 (default), 2, etc. --ca file : Certificate authority file in .pem format containing root certificate. --capath dir : A directory of trusted certificates (CAs and CRLs). --dh file : File containing Diffie Hellman parameters in .pem format (for --tls-server only). Use "openssl dhparam -out dh1024.pem 1024" to generate. --cert file : Local certificate in .pem format -- must be signed by a Certificate Authority in --ca file. --extra-certs file : one or more PEM certs that complete the cert chain. --key file : Local private key in .pem format. --tls-version-min <version> ['or-highest'] : sets the minimum TLS version we will accept from the peer. If version is unrecognized and 'or-highest' is specified, require max TLS version supported by SSL implementation. --tls-version-max <version> : sets the maximum TLS version we will use. --pkcs12 file : PKCS#12 file containing local private key, local certificate and optionally the root CA certificate. --x509-username-field : Field in x509 certificate containing the username. Default is CN in the Subject field. --verify-hash hash [algo] : Specify fingerprint for level-1 certificate. Valid algo flags are SHA1 and SHA256. --tls-cipher l : A list l of allowable TLS ciphers separated by : (optional). --tls-ciphersuites l: A list of allowed TLS 1.3 cipher suites seperated by : (optional) : Use --show-tls to see a list of supported TLS ciphers (suites). --tls-cert-profile p : Set the allowed certificate crypto algorithm profile (default=legacy). --tls-timeout n : Packet retransmit timeout on TLS control channel if no ACK from remote within n seconds (default=2). --reneg-bytes n : Renegotiate data chan. key after n bytes sent and recvd. --reneg-pkts n : Renegotiate data chan. key after n packets sent and recvd. --reneg-sec max [min] : Renegotiate data chan. key after at most max (default=3600) and at least min (defaults to 90% of max on servers and equal to max on clients). --hand-window n : Data channel key exchange must finalize within n seconds of handshake initiation by any peer (default=60). --tran-window n : Transition window -- old key can live this many seconds after new key renegotiation begins (default=3600). --single-session: Allow only one session (reset state on restart). --tls-exit : Exit on TLS negotiation failure. --tls-auth f [d]: Add an additional layer of authentication on top of the TLS control channel to protect against attacks on the TLS stack and DoS attacks. f (required) is a shared-secret key file. The optional d parameter controls key directionality, see --secret option for more info. --tls-crypt key : Add an additional layer of authenticated encryption on top of the TLS control channel to hide the TLS certificate, provide basic post-quantum security and protect against attacks on the TLS stack and DoS attacks. key (required) provides the pre-shared key file. see --secret option for more info. --tls-crypt-v2 key : For clients: use key as a client-specific tls-crypt key. For servers: use key to decrypt client-specific keys. For key generation (--genkey tls-crypt-v2-client): use key to encrypt generated client-specific key. (See --tls-crypt.) --genkey tls-crypt-v2-client [keyfile] [base64 metadata]: Generate a fresh tls-crypt-v2 client key, and store to keyfile. If supplied, include metadata in wrapped key. --genkey tls-crypt-v2-server [keyfile] [base64 metadata]: Generate a fresh tls-crypt-v2 server key, and store to keyfile --tls-crypt-v2-verify cmd : Run command cmd to verify the metadata of the client-supplied tls-crypt-v2 client key --askpass [file]: Get PEM password from controlling tty before we daemonize. --auth-nocache : Don't cache --askpass or --auth-user-pass passwords. --crl-verify crl ['dir']: Check peer certificate against a CRL. --tls-verify cmd: Run command cmd to verify the X509 name of a pending TLS connection that has otherwise passed all other tests of certification. cmd should return 0 to allow TLS handshake to proceed, or 1 to fail. (cmd is executed as 'cmd certificate_depth subject') --tls-export-cert [directory] : Get peer cert in PEM format and store it in an openvpn temporary file in [directory]. Peer cert is stored before tls-verify script execution and deleted after. --verify-x509-name name: Accept connections only from a host with X509 subject DN name. The remote host must also pass all other tests of verification. --ns-cert-type t: (DEPRECATED) Require that peer certificate was signed with an explicit nsCertType designation t = 'client' | 'server'. --x509-track x : Save peer X509 attribute x in environment for use by plugins and management interface. --keying-material-exporter label len : Save Exported Keying Material (RFC5705) of len bytes (min. 16 bytes) using label in environment for use by plugins. --remote-cert-ku v ... : Require that the peer certificate was signed with explicit key usage, you can specify more than one value. value should be given in hex format. --remote-cert-eku oid : Require that the peer certificate was signed with explicit extended key usage. Extended key usage can be encoded as an object identifier or OpenSSL string representation. --remote-cert-tls t: Require that peer certificate was signed with explicit key usage and extended key usage based on RFC3280 TLS rules. t = 'client' | 'server'. PKCS#11 Options: --pkcs11-providers provider ... : PKCS#11 provider to load. --pkcs11-protected-authentication [0|1] ... : Use PKCS#11 protected authentication path. Set for each provider. --pkcs11-private-mode hex ... : PKCS#11 private key mode mask. 0 : Try to determine automatically (default). 1 : Use Sign. 2 : Use SignRecover. 4 : Use Decrypt. 8 : Use Unwrap. --pkcs11-cert-private [0|1] ... : Set if login should be performed before certificate can be accessed. Set for each provider. --pkcs11-pin-cache seconds : Number of seconds to cache PIN. The default is -1 cache until token is removed. --pkcs11-id-management : Acquire identity from management interface. --pkcs11-id serialized-id 'id' : Identity to use, get using standalone --show-pkcs11-ids SSL Library information: --show-ciphers : Show cipher algorithms to use with --cipher option. --show-digests : Show message digest algorithms to use with --auth option. --show-engines : Show hardware crypto accelerator engines (if available). --show-tls : Show all TLS ciphers (TLS used only as a control channel). Generate a new key : --genkey secret file : Generate a new random key of type and write to file (for use with --secret, --tls-auth or --tls-crypt). Tun/tap config mode (available with linux 2.4+): --mktun : Create a persistent tunnel. --rmtun : Remove a persistent tunnel. --dev tunX|tapX : tun/tap device --dev-type dt : Device type. See tunnel options above for details. --user user : User to set privilege to. --group group : Group to set privilege to. PKCS#11 standalone options: --show-pkcs11-ids [provider] [cert_private] : Show PKCS#11 available ids. --verb option can be added *BEFORE* this. General Standalone Options: --show-gateway : Show info about default gateway.二、启动命令sudo nohup openvpn VPNConfig.ovpn > /dev/null &三、关闭命令myserver@DESKTOP-QNAP:~/programs/soft/openvpn$ ps -ef|grep openvpn root 600136 1 0 5月22 ? 00:00:00 sudo nohup openvpn VPNConfig.ovpn root 600137 600136 0 5月22 pts/1 00:00:00 sudo nohup openvpn VPNConfig.ovpn root 600138 600137 0 5月22 pts/1 00:00:10 openvpn VPNConfig.ovpn myserver 3227085 3221195 0 00:00 pts/2 00:00:00 grep --color=auto openvpn myserver@DESKTOP-QNAP:~/programs/soft/openvpn$ kill -9 600136 -

-
 GL·MT1300安装zerotier 一、更新和安装插件包opkg update && opkg install zerotier二、安装可视化插件包根据设备cpu架构类型选择对应的可视化插件包: 下载地址这里以 GL MT1300 cpu架构 MIPS 为例:下载此文件 找到对应ipk包后,也可以直接用下载文件命令下载wget https://op.supes.top/packages/mipsel_24kc/luci-app-zerotier_git-22.156.35826-edd126a_all.ipk && opkg install *.ipk三、加入网络和MOON1.加入网络zerotier-cli join 6ab565XXXXXXXXXX报错:zerotier-cli: missing port and zerotier-one.port not found in /var/lib/zerotier-one执行以下命令后会在目录 /var/lib/zerotier-one 下生成对应文件zerotier-one -d稍等之后重新加入网络即可2.查看并加入自建的moon服务器节点zerotier-cli orbit 6ab565XXXX 6ab565XXXX显示 200 orbit OK 则加入成功3.重启路由后zerotier失效问题{alert type="info"} MOON又称为自定义根服务器,通过自定义的服务器作为跳板加速内网机器之间的互相访问。我的LEDE版本是2.32,有固定公网IP,为了提高ZeroTier在不同子网之间互访的速度,建立MOON节点就非常有必要。在启用ZeroTier后,我发现ZeroTier安装目录 /var/lib/zerotier-one (这个目录实际链接到 /var/lib/zerotier-one_sample_config )是临时目录 ,在 重启后就自动删除 ,必须修改配置文件,才能保留MOON的配置。{/alert}(1)修改配置文件 /etc/config/zerotier ,加入下面一行选项:option config_path '/etc/zerotier'option enabled 0 改为 option enabled 1config zerotier 'sample_config' option enabled '1' #option port '9993' # Join a public network called Earth list join '6ab565XXXXXXXXXX' option nat '1' # Generate secret on first start option secret 'generate' # persistent configuration folder (for ZT controller mode) # 配置文件路径,启动后会在这个指定路径生成配置文件 option config_path '/etc/zerotier' 启动zerotier/etc/init.d/zerotier start(2)生成moon.json文件zerotier-idtool generate identity.secret identity.public && zerotier-idtool initmoon identity.public >>moon.json(3)修改moon.json文件 stableEndpoints stableEndpoints 为 IP/PORT 结构,端口号(默认9993)为moon服务实际端口号{ "id": "1bf1ab4257", "objtype": "world", "roots": [ { "identity": "4f1a21bb57:0:f4e92d2ec3b3db486fd9b3d1d1d4fe75d3b34908abfed746d2ae2d47874abb54e39fdaa03913ae45ad73d393f4b649cfad3639149b41720714aac79e11b8c425", "stableEndpoints": [ "120.120.120.175/9995" ] } ], "signingKey": "7165a5a68ec892f9f1b48bd804b6f188145c81d9f0afc84ffc6f05c06f235d57c87f6df0d7e21665f186e2bd273d76ae00b7eb2e400e9ebb567c6ec0c948dec8", "signingKey_SECRET": "653caf87483f7da078fc1ae3a69c8677f05c547d587bd39ebd3ddba1ea68aef5b6acad157d35e0586f5ff9f7c03e50bd434236e9f00dd57e35c8fffca939d404", "updatesMustBeSignedBy": "7165aec892f9f1b48bd804b6f188145c81d9f0afc84ffc6f05c06f235d57c87f6df0d7e21665f186e2bd273d5a680b7eb2e40076ae0e9ebb567c6ec0c948dec8", "worldType": "moon" }(4)生成签名文件zerotier-idtool genmoon moon.json在当前目录下生成签名文件 00000005ff20a0f6.moon (5)将MOON节点加入网络在 /etc/zerotier 目录建立 moons.d 子目录,将生成的 00000005ff20a0f6.moon 复制到该文件夹中,并重启设备。(6)测试验证查看是否在MOON下运行,执行以下命令:zerotier-cli listpeersPLANET :行星服务器,Zerotier 各地的根服务器,有日本、新加坡等地MOON :卫星级服务器,用户自建的私有根服务器,起到中转加速的作用LEAF :相当于各个枝叶,就是每台连接到该网络的机器节点如果某一行显示有MOON字样,就证明MOON已被本机标识了。#zt5lnhygsv iptables -I FORWARD -i zt5lnhygsv -j ACCEPT iptables -I FORWARD -o zt5lnhygsv -j ACCEPT iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -o zt5lnhygsv -j MASQUERADE
GL·MT1300安装zerotier 一、更新和安装插件包opkg update && opkg install zerotier二、安装可视化插件包根据设备cpu架构类型选择对应的可视化插件包: 下载地址这里以 GL MT1300 cpu架构 MIPS 为例:下载此文件 找到对应ipk包后,也可以直接用下载文件命令下载wget https://op.supes.top/packages/mipsel_24kc/luci-app-zerotier_git-22.156.35826-edd126a_all.ipk && opkg install *.ipk三、加入网络和MOON1.加入网络zerotier-cli join 6ab565XXXXXXXXXX报错:zerotier-cli: missing port and zerotier-one.port not found in /var/lib/zerotier-one执行以下命令后会在目录 /var/lib/zerotier-one 下生成对应文件zerotier-one -d稍等之后重新加入网络即可2.查看并加入自建的moon服务器节点zerotier-cli orbit 6ab565XXXX 6ab565XXXX显示 200 orbit OK 则加入成功3.重启路由后zerotier失效问题{alert type="info"} MOON又称为自定义根服务器,通过自定义的服务器作为跳板加速内网机器之间的互相访问。我的LEDE版本是2.32,有固定公网IP,为了提高ZeroTier在不同子网之间互访的速度,建立MOON节点就非常有必要。在启用ZeroTier后,我发现ZeroTier安装目录 /var/lib/zerotier-one (这个目录实际链接到 /var/lib/zerotier-one_sample_config )是临时目录 ,在 重启后就自动删除 ,必须修改配置文件,才能保留MOON的配置。{/alert}(1)修改配置文件 /etc/config/zerotier ,加入下面一行选项:option config_path '/etc/zerotier'option enabled 0 改为 option enabled 1config zerotier 'sample_config' option enabled '1' #option port '9993' # Join a public network called Earth list join '6ab565XXXXXXXXXX' option nat '1' # Generate secret on first start option secret 'generate' # persistent configuration folder (for ZT controller mode) # 配置文件路径,启动后会在这个指定路径生成配置文件 option config_path '/etc/zerotier' 启动zerotier/etc/init.d/zerotier start(2)生成moon.json文件zerotier-idtool generate identity.secret identity.public && zerotier-idtool initmoon identity.public >>moon.json(3)修改moon.json文件 stableEndpoints stableEndpoints 为 IP/PORT 结构,端口号(默认9993)为moon服务实际端口号{ "id": "1bf1ab4257", "objtype": "world", "roots": [ { "identity": "4f1a21bb57:0:f4e92d2ec3b3db486fd9b3d1d1d4fe75d3b34908abfed746d2ae2d47874abb54e39fdaa03913ae45ad73d393f4b649cfad3639149b41720714aac79e11b8c425", "stableEndpoints": [ "120.120.120.175/9995" ] } ], "signingKey": "7165a5a68ec892f9f1b48bd804b6f188145c81d9f0afc84ffc6f05c06f235d57c87f6df0d7e21665f186e2bd273d76ae00b7eb2e400e9ebb567c6ec0c948dec8", "signingKey_SECRET": "653caf87483f7da078fc1ae3a69c8677f05c547d587bd39ebd3ddba1ea68aef5b6acad157d35e0586f5ff9f7c03e50bd434236e9f00dd57e35c8fffca939d404", "updatesMustBeSignedBy": "7165aec892f9f1b48bd804b6f188145c81d9f0afc84ffc6f05c06f235d57c87f6df0d7e21665f186e2bd273d5a680b7eb2e40076ae0e9ebb567c6ec0c948dec8", "worldType": "moon" }(4)生成签名文件zerotier-idtool genmoon moon.json在当前目录下生成签名文件 00000005ff20a0f6.moon (5)将MOON节点加入网络在 /etc/zerotier 目录建立 moons.d 子目录,将生成的 00000005ff20a0f6.moon 复制到该文件夹中,并重启设备。(6)测试验证查看是否在MOON下运行,执行以下命令:zerotier-cli listpeersPLANET :行星服务器,Zerotier 各地的根服务器,有日本、新加坡等地MOON :卫星级服务器,用户自建的私有根服务器,起到中转加速的作用LEAF :相当于各个枝叶,就是每台连接到该网络的机器节点如果某一行显示有MOON字样,就证明MOON已被本机标识了。#zt5lnhygsv iptables -I FORWARD -i zt5lnhygsv -j ACCEPT iptables -I FORWARD -o zt5lnhygsv -j ACCEPT iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -o zt5lnhygsv -j MASQUERADE
您的IP: